1. Acuna, R., & Bansal, A. (2022). Using programming autograder formative data to understand student growth. In 2022 IEEE frontiers in education conference (FIE) (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
2. Adewale, O. S., Agbonifo, O. C., Ibam, E. O., Makinde, A. I., Boyinbode, O. K., Ojokoh, B. A., Olabode, O., Omirin, M. S., & Olatunji, S. O. (2024). Design of a personalised adaptive ubiquitous learning system. Interactive Learning Environments, 32, 208–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2084114
3. Ainapure, B., Pise, R., & Singh, D. (2022). Machine learning based code assessment systems. In 2022 5th international conference on contemporary computing and informatics (IC3I) (pp. 1568–1574). IEEE.
4. Al Hajj, J., & Sah, M. (2023). Assessing the impact of ChatGPT in a PHP programming course. In 2023 7th International Symposium on Innovative Approaches in Smart Technologies (ISAS) (pp. 1–10). IEEE.
5. Al-Imarah, A. A., & Shields, R. (2019). MOOCs, disruptive innovation and the future of higher education: A conceptual analysis. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 56, 258–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2018.1443828
6. Alshaikh, Z., Tamang, L. J., & Rus, V. (2020). Experiments with a Socratic intelligent tutoring system for source code understanding. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference (FLAIRS-32).
7. Alsuhaymi, D. S., & Alotaibi, O. M. (2023). Gamification’s Efficacy in Enhancing Students’ HTML Programming Skills and Academic Achievement Motivation. J. Educ. E-Learn. Res., 10, 397–407. https://doi.org/10.20448/jeelr.v10i4.4984
8. Alzoubi, O., Fossati, D., Eugenio, B. D., Green, N., & Chen, L. (2013). Predicting students’ performance and problem solving behavior from iList log data. In Proceedings of the 21st international conference on computers in education (ICCE 2013).
9. Amit, S., Karim, R., & Kafy, A. A. (2022). Mapping emerging massive open online course (MOOC) markets before and after COVID 19: A comparative perspective from Bangladesh and India. Spatial Information Research, 30, 655–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-022-00463-4
10. An, Y. (2020). A history of instructional media, instructional design, and theories. International Journal of Technology in Education, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.46328/ijte.35
11. Anand, V. K., Rahiman, S. K. A., Ben George, E., & Huda, A. S. (2018). Recursive clustering technique for students’ performance evaluation in programming courses. In 2018 Majan international conference (MIC) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
12. Angelovski, D., Stankov, E., & Jovanov, M. (2021). DEMAx tool based on an improved model for semiautomatic C/C++ source code assessment. In 2021 the 6th international conference on information and education innovations (pp. 68–73). ACM.
13. Anthony, A., & Raney, M. (2012). Bayesian network analysis of computer science grade distributions. In Proceedings of the 43rd ACM technical symposium on computer science education (pp. 649–654). ACM.
14. Anwar, S., Butt, A. A., & Menekse, M. (2023). Utilizing automated scaffolding strategies to improve students’ reflections writing process. In 2023 IEEE frontiers in education conference (FIE) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
15. Arakawa, K., Hao, Q., Deneke, W., Cowan, I., Wolfman, S., & Peterson, A. (2022). Early identification of student struggles at the topic level using context-agnostic features. In Proceedings of the 53rd ACM technical symposium on computer science education (pp. 147–153). ACM.
16. Arango, M. C., Hincapie-Otero, M., Hardeman, K., Shao, B., Starbird, L., & Starbird, C. (2024). Special considerations for the use of AI tools by PEERs as a learning and communication aid. J. Cell. Physiol., 239, e31339.
17. Aremu, V. I., Okuntade, J. O., & Ebimomi, O. E. (2022). Computer Programming Language as Tool for Developing Primary School Pupils’ Academic and Thinking Skills. Ilorin Journal of Education, 42(2), 69–74.
18. Arhandi, P. P., Firdausi, A. T., Andoko, B. S., & Masykuro, N. S. A. Q. (2023). Development of SQL similarity with multiple answer keys for the automated assessment process in the SQLearn application. In 2023 sixth international conference on vocational education and electrical engineering (ICVEE) (pp. 19–24). IEEE.
19. Arun, G., Perumal, V., Urias, F., Ler, Y. E., Tan, B. W. T., Vallabhajosyula, R., Tan, E., Ng, O., Ng, K. B., & Mogali, S. R. (2024). ChatGPT versus a customized AI chatbot (Anatbuddy) for anatomy education: A comparative pilot study. Anat. Sci. Educ., 17, 1396–1405.
20. Au, T.-W., Salihin, R., & Saiful, O. (2022). Performance prediction of learning programming - machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the 30th international conference on computers in education.
21. Azcona, D., & Smeaton, A. F. (2017). Targeting at-risk students using engagement and effort predictors in an introductory computer programming course. In É. Lavoué, H. Drachsler, K. Verbert, J. Broisin, & M. Pérez-Sanagustín (Eds.), Data driven approaches in digital education (Vol. 10474, pp. 361–366). Springer International Publishing.
22. Aziz, A. A., Ismail, U. H., & Ahmad, F. (2013). Mining Students’ Academic Performance.
23. Bada, D., & Olusegun, S. (2015). Constructivism learning theory: A paradigm for teaching and learning. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 5, 66–70.
24. Bahrehvar, M., & Moshirpour, M. (2023). Agile teaching: Automated student support and feedback generation. In 2023 IEEE frontiers in education conference (FIE) (pp. 1–9). IEEE.
25. Baig, Z., & Zeadally, S. (2019). Cyber-security risk assessment framework for critical infrastructures. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput, 25(1), 121–130.
26. Baker, R. S., & Yacef, K. (2009). The state of educational data mining in 2009: A review and future visions. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.3554657
27. Barbosa, A. D. A., Costa, E. D. B., & Brito, P. H. (2018). Adaptive clustering of codes for assessment in introductory programming courses. In R. Nkambou, R. Azevedo, & J. Vassileva (Eds.), Intelligent tutoring systems (Vol. 10858, pp. 13–22). Springer International Publishing.
28. Beck, P. J., Jean Mohammadi-Aragh, M., Archibald, C., Jones, B. A., & Barton, A. (2018). Real-time metacognition feedback for introductory programming using machine learning. In 2018 IEEE frontiers in education conference (FIE) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
29. Becker, B. A., Denny, P., Finnie-Ansley, J., Luxton-Reilly, A., Prather, J., & Santos, E. A. (2023). Generative ai in introductory programming. In "Computer Science Curricula 2023, CS2023, Curricular Practices Volume". ACM. https://csed.acm.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Generative-AI-Nov-2023-Version.pdf
30. Becker, B. A., Denny, P., Finnie-Ansley, J., Luxton-Reilly, A., Prather, J., & Santos, E. A. (2023). Programming is hard - or at least it used to be: Educational opportunities and challenges of AI code generation. In Proceedings of the 54th ACM technical symposium on computer science education V. 1 (pp. 500–506). ACM.
31. Behera, A., Matthew, P., Keidel, A., Vangorp, P., Fang, H., & Canning, S. (2020). Associating facial expressions and upper-body gestures with learning tasks for enhancing intelligent tutoring systems. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 30, 236–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-020-00195-2
32. Boguslawski, S., Deer, R., & Dawson, M. G. (2025). Programming education and learner motivation in the age of generative AI: student and educator perspectives. Information and Learning Sciences, 126(1/2), 91–109. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILS-10-2023-0163
33. Bond, J., & Dirkin, K. (2020). What models are instructional designers using today? Journal of Applied Instructional Design, 9. https://doi.org/10.51869/92jbkd
34. Buschetto Macarini, L. A., Cechinel, C., Batista Machado, M. F., Faria Culmant Ramos, V., & Munoz, R. (2019). Predicting students success in blended learning—evaluating different interactions inside learning management systems. Applied Sciences, 9(24), 5523. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245523
35. Carter, A. S., Hundhausen, C. D., & Adesope, O. (2015). The normalized programming state model: Predicting student performance in computing courses based on programming behavior. In Proceedings of the eleventh annual international conference on international computing education research (pp. 141–150). ACM.
36. Carvalho, W., Tomov, M. S., de Cothi, W., Barry, C., & Gershman, S. J. (2024). Predictive Representations: Building Blocks of Intelligence. Neural Comput., 36, 2225–2298.
37. Chang, E. Y. (2023). Examining gpt-4: Capabilities, implications and future directions. In The 10th International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence.
38. Chang, X., Wang, B., & Hui, B. (2022). Towards an automatic approach for assessing program competencies. In LAK22: 12th international learning analytics and knowledge conference (pp. 119–129). ACM.
39. Chen, D., Liu, W., & Liu, X. (2024). What drives college students to use AI for L2 learning? Modeling the roles of self-efficacy, anxiety, and attitude based on an extended technology acceptance model. Acta Psychol., 249, 104442.
40. Chen, L., Chen, P., & Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access, 8, 75264–75278. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988510
41. Chen, M., Tworek, T., Jun, H., Grover, C., McCloskey, J., Sathe, S., Schoenholz, T., Sutskever, I., & Chen, J. (2021). Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03374.
42. Cheng, A. Y., Tanimura, E., Tey, J., Wu, A. C., & Brunskill, E. (2024). Brief, just-in-time teaching tips to support computer science tutors. In Proceedings of the 55th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1 (pp. 200–206). ACM.
43. Chiappa, A. S., Tano, P., Patel, N., Ingster, A., Pouget, A., & Mathis, A. (2024). Acquiring musculoskeletal skills with curriculum-based reinforcement learning. Neuron, 112(20), 3969–3983.e5.
44. Chiheb, F., Boumahdi, F., Bouarfa, H., & Boukraa, D. (2017). Predicting students performance using decision trees: Case of an Algerian University. In 2017 international conference on mathematics and information technology (ICMIT) (pp. 113–121). IEEE.
45. Choudhuri, R., Liu, D., Steinmacher, I., Gerosa, M., & Sarma, A. (2024). How far are we? The triumphs and trials of generative AI in learning software engineering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 46th International Conference on Software Engineering (pp. 1–13). IEEE.
46. Choudhury, A., & Chaudhry, Z. (2024). Large Language Models and User Trust: Consequence of Self-Referential Learning Loop and the Deskilling of Health Care Professionals. J. Med. Internet. Res., 26, e56764.
47. Clow, D. (2013). An overview of learning analytics. Teaching in Higher Education, 18(6), 683–695. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562517.2013.827653
48. Coffman, J., de Freitas, A. A., Hill, J. M., & Weingart, T. (2023). Visual vs. textual programming languages in CS0.5: Comparing student learning with and student perception of RAPTOR and Python. In Proceedings of the 54th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1 (pp. 32–38). ACM.
49. Combéfis, S. (2022). Automated code assessment for education: Review, classification and perspectives on techniques and tools. Software, 1(1), 3–30. https://doi.org/10.3390/software1010002
50. Costa, E. B., Fonseca, B., Santana, M. A., De Araújo, F. F., & Rego, J. (2017). Evaluating the effectiveness of educational data mining techniques for early prediction of st... (Incomplete reference)
51. Cubillos, C., Mellado, R., Cabrera-Paniagua, D., & Urra, E. (2025). Generative Artificial Intelligence in Computer Programming: Does it enhance learning, motivation, and the learning environment? IEEE Access, 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3532883
52. D’mello, S., & Graesser, A. (2013). AutoTutor and affective AutoTutor: Learning by talking with cognitively and emotionally intelligent computers that talk back. ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems (TiiS), 2(4), 1–39.
53. Daun, M., Brings, J., Obe, P. A., & Stenkova, V. (2021). Reliability of self-rated experience and confidence as predictors for students’ performance in software engineering: Results from multiple controlled experiments on model comprehension with graduate and undergraduate students. Empir. Softw. Eng., 26, 80.
54. De Silva, D. I., Vidhanaarachchi, S., Kariyawasam, S. B., Dasanayake, L. R. S., Thawalampola, O. D., & Jayasuriya, T. D. D. H. (2023). CodeCoach: An interactive programming assistance tool. J. Propuls. Technol., 44(4), 7281–7288.
55. Dwyer, C. P., Hogan, M. J., & Stewart, I. (2011). The promotion of critical thinking skills through argument mapping. In C. P. Horvath & J. M. Forte (Eds.), Critical Thinking Editor.
56. Facione, P. (1990). Critical thinking: A statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research Findings and Recommendations. American Philosophical Association.
57. Fan, Z., Noller, Y., Dandekar, A., & Roychoudhury, A. (2023). Intelligent tutoring system: Experience of linking software engineering and programming teaching. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.05472.
58. Firretto, C., Konak, A., & Well, V. (2024). Theoretical Perspectives on Critical Thinking: Implications for Entrepreneurship Education Research and Practice. VentureWell. https://venturewell.org/wp-
59. Grandchamp des Raux, H., Ghilardi, T., Soderberg, C., & Ossmy, O. (2024). The role of action concepts in physical reasoning: Insights from late childhood. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci., 379(1896), 20230154.
60. Grover, S., & Pea, R. (2013). Computational Thinking in K–12: A Review of the State of the Field. Educational Researcher, 42(1), 38–43. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X12463051
61. Haindl, P., & Weinberger, G. (2024). Students’ experiences of using ChatGPT in an undergraduate programming course. IEEE Access, 12, 43519–43529.
62. Hao, Q., Smith IV, D. H., Ding, L., Ko, A., Ottaway, C., Wilson, J., & Greer, T. (2022). Towards understanding the effective design of automated formative feedback for programming assignments. Comput. Sci. Educ., 32(1), 105–127.
63. Hashmi, N., Li, Z., Parise, S., & Shankaranarayanan, G. (2024). Generative AI's impact on programming students: frustration and confidence across learning styles. Issues in Information Systems, 25(3).
64. Hultberg, P. T., Santandreu Calonge, D., Kamalov, F., & Smail, L. (2024). Comparing and assessing four AI chatbots’ competence in economics. PLoS ONE, 19(1), e0297804.
65. Huse, N., & Le, N.-T. (2016). The formal models for the socratic method. In Advanced Computational Methods for Knowledge Engineering: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer Science, Applied Mathematics and Applications, ICCSAMA 2016, 2-3 May, 2016, Vienna, Austria (pp. 181–193). Springer.
66. Hussain, K., Nso, N., Tsourdinis, G., Haider, S., Mian, R., Sanagala, T., Erwin, J. P., 3rd, & Pursnani, A. (2024). A systematic review and meta-analysis of left atrial strain in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and its prognostic utility. Curr. Probl. Cardiol., 49(1 Pt C), 102146.
67. Illouz, T., Ascher, L. A. B., Madar, R., & Okun, E. (2024). Unbiased analysis of spatial learning strategies in a modified Barnes maze using convolutional neural networks. Sci. Rep., 14, 15944.
68. Jallad, S. T., Alsaqer, K., Albadareen, B. I., & Al-Maghaireh, D. (2024). Artificial intelligence tools utilized in nursing education: Incidence and associated factors. Nurse Educ. Today, 142, 106355.
69. Jarry Trujillo, C., Vela Ulloa, J., Escalona Vivas, G., Grasset Escobar, E., Villagran Gutierrez, I., Achurra Tirado, P., & Varas Cohen, J. (2024). Surgeons vs ChatGPT: Assessment and Feedback Performance Based on Real Surgical Scenarios. J. Surg. Educ., 81(6), 960–966.
70. Kazemitabaar, M., Hou, X., Henley, A., Ericson, B. J., Weintrop, D., & Grossman, T. (2023). How novices use LLM-based code generators to solve CS1 coding tasks in a self-paced learning environment. In Proceedings of the 23rd Koli Calling International Conference on Computing Education Research (12p).
71. Khan, K., & Katarya, R. (2025). WS-BiTM: Integrating White Shark Optimization with Bi-LSTM for enhanced autism spectrum disorder diagnosis. J. Neurosci. Methods, 413, 110319.
72. Kitchenham, B., Brereton, O. P., Budgen, D., Turner, M., Bailey, J., & Linkman, S. (2009). Systematic literature reviews in software engineering—A systematic literature review. Inf. Softw. Technol., 51(1), 7–15.
73. Koch, E. T., Cheng, J., Ramandi, D., Sepers, M. D., Hsu, A., Fong, T., Murphy, T. H., Yttri, E., & Raymond, L. A. (2024). Deep behavioural phenotyping of the Q175 Huntington disease mouse model: Effects of age, sex, and weight. BMC Biol., 22, 121.
74. Konak, A., & Clarke, C. J. S. F. (2023). Augmenting Critical Thinking Skills in Programming Education through Leveraging Chat GPT: Analysis of its Opportunities and Consequences. In 2023 ASEE Mid Atlantic Section Fall Conference (pp. 1–10). https://doi.org/10.18260/1-2--45117
75. Konak, A., Kulturel-Konak, S., & Liu, H. (2023). Entrepreneurial Mindset & Innovative Thinking Skills. In ASEE Zone 1 Conference-Spring State College, PA (pp. 1–10).
76. Kosar, T., Ostojić, D., Liu, Y. D., & Mernik, M. (2024). Computer science education in the ChatGPT era: Experiences from an experiment in a programming course for novice programmers. Mathematics, 12(4), 629.
77. Kristiansen, N. G., Nicolajsen, S. M., & Brabrand, C. (2023). Feedback on student programming assignments: Teaching assistants vs. automated assessment tool. In Proceedings of the 23rd Koli Calling International Conference on Computing Education Research (10p).
78. Lawson McLean, A. (2024). Constructing knowledge: The role of AI in medical learning. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc., 31(11), 1797–1798.
79. Leinonen, J., Denny, P., MacNeil, S., Sarsa, S., Bernstein, S., Kim, J., Tran, A., & Hellas, A. (2023). Comparing code explanations created by students and large language models. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education V. 1 (pp. 124–130).
80. Li, W., Zhang, X., Li, J., Yang, X., Li, D., & Liu, Y. (2024). An explanatory study of factors influencing engagement in AI education at the K-12 Level: An extension of the classic TAM model. Sci. Rep., 14, 13922.
81. Liu, D., Calver, J., & Craig, M. (2024). A Static Analysis Tool in CS1: Student Usage and Perceptions of PythonTA. In Proceedings of the 26th Australasian Computing Education Conference (pp. 172–181). ACM.
82. Lytra, I. S. (2020). Reinventing Socratic Irony’s Educational Character [Doctoral dissertation, University of Edinburgh].
83. Ma, Q., Shen, H., Koedinger, K., & Wu, T. (2023). How to teach programming in the AI era? Using LLMs as a teachable agent for debugging. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.05292.
84. Määttä, S. (2024). Generative artificial intelligence in programming: A scoping review of cognitive aspects [Master’s thesis, University of Oulu].
85. Macnamara, B. N., Berber, I., Cavusoglu, M. C., Krupinski, E. A., Nallapareddy, N., Nelson, N. E., Smith, P. J., Wilson-Delfosse, A. L., & Ray, S. (2024). Does using artificial intelligence assistance accelerate skill decay and hinder skill development without performers’ awareness? Cogn. Res. Princ. Implic., 9, 46.
86. Maher, M. L., Tadimalla, S. Y., & Dhamani, D. (2023). An Exploratory Study on the Impact of AI tools on the Student Experience in Programming Courses: An Intersectional Analysis Approach. In 2023 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
87. Maldonado-Trapp, A., & Bruna, C. (2024). The Evolution of Active Learning in Response to the Pandemic: The Role of Technology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 1458, 247–261.
88. Manfredi, G., Erra, U., & Gilio, G. (2023). A mixed reality approach for innovative pair programming education with a conversational AI virtual avatar. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering (pp. 450–454). ACM.
89. Manley, E. D., Urness, T., Migunov, A., & Reza, M. A. (2024). Examining student use of AI in CS1 and CS2. J. Comput. Sci. Coll., 39(6), 41–51.
90. Marchesi, S., De Tommaso, D., Kompatsiari, K., Wu, Y., & Wykowska, A. (2024). Tools and methods to study and replicate experiments addressing human social cognition in interactive scenarios. Behav. Res. Methods, 56, 7543–7560.
91. McLoughlin, C., & Lee, M. J. (2010). Personalised and self regulated learning in the Web 2.0 era: International exemplars of innovative pedagogy using social software. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 26(1).
92. Mellado, R., Cubillos, C., & Ahumada, G. (2024). Effectiveness of Generative Artificial Intelligence in learning programming to higher education students. In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Automation/XXVI Congress of the Chilean Association of Automatic Control (ICA-ACCA) (pp. 1–7). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICA-ACCA62622.2024.10766746
93. Morten, N. (2023). Metacognition and Reflective Teaching: A Synergistic Approach to Fostering Critical Thinking Skills. Research and Advances in Education, 2(9), 1–14.
94. Moulin, T. C. (2024). Learning with AI Language Models: Guidelines for the Development and Scoring of Medical Questions for Higher Education. J. Med. Syst., 48, 45.
95. Mukherjee, M., Le, N. T., Chow, Y.-W., & Susilo, W. (2024). Strategic approaches to cybersecurity learning: A study of educational models and outcomes. Information, 15(2), 117.
96. Muthmainnah, M., Cardoso, L., Alsbbagh, Y. A. M. R., Al Yakin, A., & Apriani, E. (2024). Advancing Sustainable Learning by Boosting Student Self-regulated Learning and Feedback Through AI-Driven Personalized in EFL Education. In International Conference on Explainable Artificial Intelligence in the Digital Sustainability (pp. 36–54). Springer.
97. Naamati-Schneider, L. (2024). Enhancing AI competence in health management: Students’ experiences with ChatGPT as a learning Tool. BMC Med. Educ., 24, 598.
98. Nassar, S. (2019). Future aspects of critical thinking and AI. In Proceedings of WRFASE International Conference.
99. Nguyen, S., Babe, H. M., Zi, Y., Guha, A., Anderson, C. J., & Feldman, M. Q. (2024). How beginning programmers and code LLMs (mis) read each other. In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1–26). ACM.
100. Nguyen, T. N. T., Lai, N. V., & Nguyen, Q. (2024). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education: A Case Study on ChatGPT’s Influence on Student Learning Behaviors. Educational Process: International Journal, 13(2), 105–121. https://doi.org/10.22521/edupij.2024.132.7
101. Obermüller, F., Greifenstein, L., & Fraser, G. (2023). Effects of automated feedback in scratch programming tutorials. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education V. 1 (pp. 396–402).
102. Ododo, E. P., Essien, N. P., & Bassey, A. E. (2024). Effect of Generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based tool utilization and students’ programming self-efficacy and computational thinking skills in JAVA programming course in Nigeria Universities. International Journal of Contemporary Africa Research Network, 2(1).
103. Ouaazki, A., Bergram, K., Farah, J. C., Gillet, D., & Holzer, A. (2024). Generative AI-enabled conversational interaction to support self-directed learning experiences in transversal computational thinking. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM Conference on Conversational User Interfaces (pp. 1–12).
104. Ouyang, F., Guo, M., Zhang, N., Bai, X., & Jiao, P. (2024). Comparing the effects of instructor manual feedback and ChatGPT intelligent feedback on collaborative programming in China’s higher education. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol., 17, 2227–2239.
105. Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., McGuinness, L. A., ... Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, 372, n71.
106. Pankiewicz, M., & Baker, R. S. (2023). Large language models (GPT) for automating feedback on programming assignments. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.00150.
107. Parsons, D., & Haden, P. (2007). Programming osmosis: Knowledge transfer from imperative to visual programming environments. In Proceedings of The Twentieth Annual NACCQ Conference (pp. 209–215). Citeseer.
108. Peng, S., Kalliamvakou, E., Cihon, P., & Demirer, M. (2023). The impact of AI on developer productivity: Evidence from GitHub Copilot. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.06590.
109. Pinheiro, E. D., Sato, J. R., Junior, R., Barreto, C., & Oku, A. Y. A. (2024). Eye-tracker and fNIRS: Using neuroscientific tools to assess the learning experience during children’s educational robotics activities. Trends Neurosci. Educ., 36, 100234.
110. Premkumar, P. P., Yatigammana, M. R. K. N., & Kannangara, S. (2023). Impact of Generative AI on Critical Thinking Skills in Undergraduates: A Systematic Review. The Journal of Desk Research Review and Analysis – JDRRA, The Library, University of Kelaniya, 1(1), 01–22.
111. Qureshi, B. (2023). Exploring the use of chatgpt as a tool for learning and assessment in undergraduate computer science curriculum: Opportunities and challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.11214.
112. Rasul, T., Waheed, H., Iqbal, J., & Waheed, F. (2023). The role of ChatGPT in higher education: Benefits, challenges, and future research directions. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching, 6(1), 41–56.
113. Roll, I., & Wylie, R. (2016). Evolution and Revolution in Artificial Intelligence in Education. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 26(2), 582–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-016-0110-3
114. Scherer, R., Siddiq, F., & Sánchez-Scherer, B. (2021). Some Evidence on the Cognitive Benefits of Learning to Code. Frontiers in Psychology, Opinion, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.559424
115. Scholl, A., & Kiesler, N. (2024). How novice programmers use and experience ChatGPT when solving programming exercises in an introductory course. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.20792.
116. Seferoglu, S. S. (2021). A comparison of solo and pair programming in terms of flow experience, coding quality, and coding achievement. J. Educ. Comput. Res., 58(7), 1448–1466.
117. Silva, C. A. G. d., Ramos, F. N., Moraes, R. V. d., & Santos, E. L. d. (2024). ChatGPT: Challenges and benefits in software programming for higher education. Sustainability, 16(3), 1245.
118. Singaram, V. S., Pillay, R., & Mbobnda Kapche, E. L. (2024). Exploring the role of digital technology for feedback exchange in clinical training: A scoping review. Syst. Rev., 13, 298.
119. Singh, A., Brooks, C., & Wang, X. (2024). The impact of student-AI collaborative feedback generation on learning outcomes. In AI for Education: Bridging Innovation and Responsibility at the 38th AAAI Annual Conference on AI.
120. Sinha, A., Goyal, S., Sy, Z., Kuperus, R., Dickey, E., & Bejarano, A. (2024). BoilerTAI: A platform for enhancing instruction using generative AI in educational forums. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.13196.
121. Styve, A., Virkki, O. T., & Naeem, U. (2024). Developing Critical Thinking Practices Interwoven with Generative AI Usage in an Introductory Programming Course. In 2024 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) (pp. 01–08). IEEE.
122. Sun, G. H. (2024). Prompt Engineering for Nurse Educators. Nurse Educ., 49(5), 293–299.
123. Suriano, R., Plebe, A., Acciai, A., & Fabio, R. A. (2025). Student interaction with ChatGPT can promote complex critical thinking skills. Learning and Instruction, 95, 102011.
124. Talagala, N. (2024, November 30). How AI Will (or Should) Change Computer Science Education. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/nishatalagala/2024/11/30/how-ai-will-or-should-change-computer-science-education/
125. Tioh, J.-N., Mina, M., & Jacobson, D. W. (2017). Cyber security training a survey of serious games in cyber security. In 2017 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
126. Wang, W., Ning, H., Zhang, G., Liu, L., & Wang, Y. (2024). Rocks coding, not development: A human-centric, experimental evaluation of LLM-supported SE tasks. Proc. ACM Softw. Eng., 1(SEET), 699–721.
127. Wang, X., Wang, Y., Yang, F., Le, W., & Wang, S. (2022). Measuring programming ability for novice programmers. J. Internet Technol., 23(3), 573–581.
128. Wang, Z., Wang, S., Wang, M., & Sun, Y. (2024). Design of application-oriented disease diagnosis model using a meta-heuristic algorithm. Technol. Health Care, 32(6), 4041–4061.
129. Weintrop, D., Beheshti, E., Horn, M., Orton, K., Jona, K., Trouille, L., & Wilensky, U. (2016). Defining computational thinking for mathematics and science classrooms. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 25, 127–147.
130. Williams, P. (2023). Education Evolution: Pedagogical Techniques for the Modern World. International Journal of Research and Review Techniques, 2(2), 7–13.
131. Xue, Y., Chen, H., Bai, G. R., Tairas, R., & Huang, Y. (2024). Does ChatGPT help with introductory programming? An experiment of students using ChatGPT in CS1. In Proceedings of the 46th International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering Education and Training (pp. 331–341).
132. Yilmaz, R., & Yilmaz, F. G. K. (2023). Augmented intelligence in programming learning: Examining student views on the use of ChatGPT for programming learning. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans, 1(2), 100005.
133. Zha, F., Wang, Y., Mao, L., & Liu, J. (2023). Can university marks measure programming skills for novice programmers? An exploratory study. J. Internet Technol., 24(4), 1189–1197.
134. Zimmerman, B. J. (2002). Becoming a Self-Regulated Learner: An Overview. Theory Into Practice, 41(2), 64–70. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip4102_2
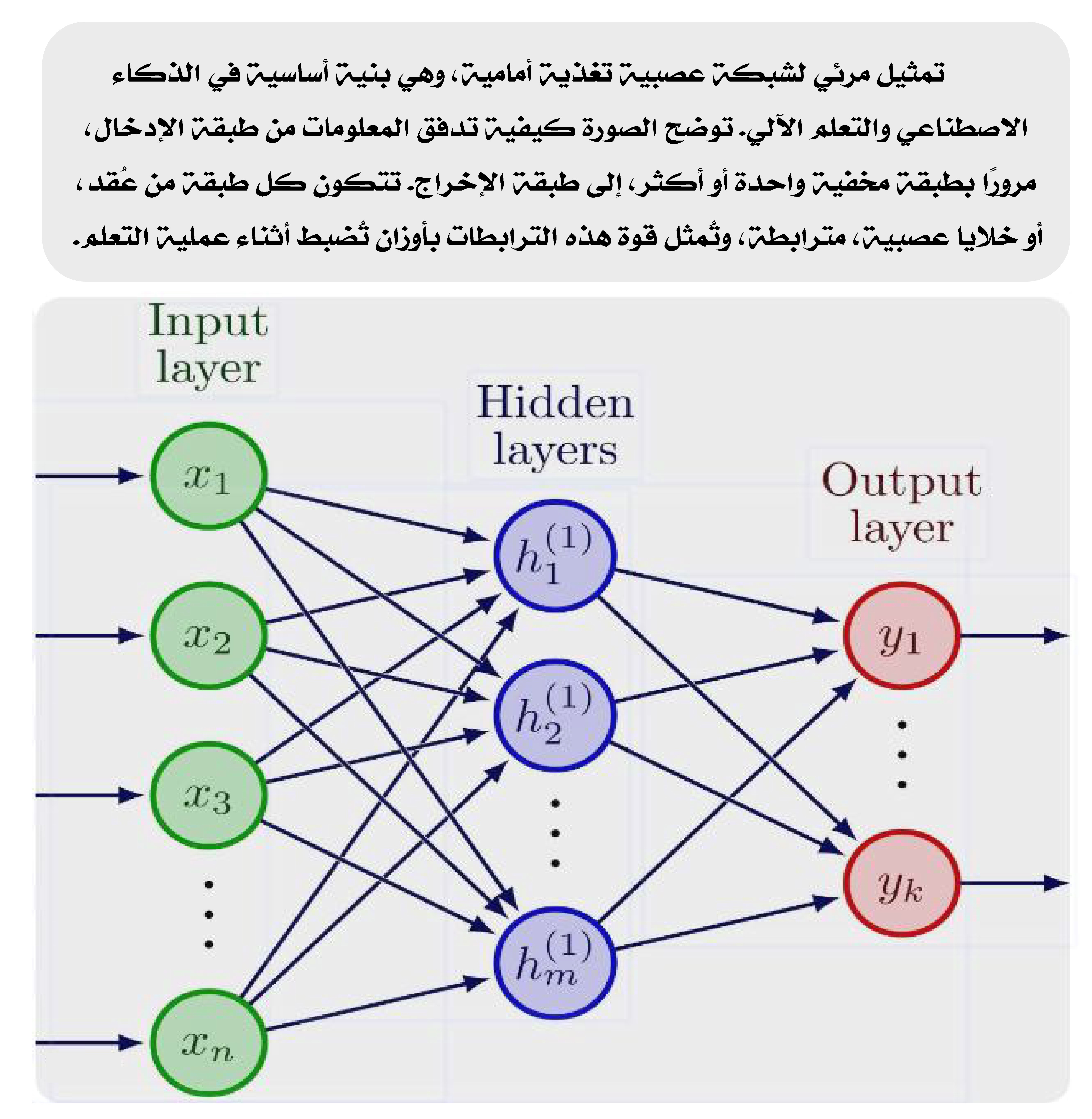 ون كل طبقة من عُقد، أو خلايا عصبية، مترابطة، وتُمثل قوة هذه الترابطات بأوزان تُضبط أثناء عملية التعلم.
ون كل طبقة من عُقد، أو خلايا عصبية، مترابطة، وتُمثل قوة هذه الترابطات بأوزان تُضبط أثناء عملية التعلم.